Articles
Nissl staining
Nissl Staining
This staining method is named after the german neurologist Franz Nissl . on the other hand , Nissl is an old term for endoplasmic reticulum. Nissl staining is used to expose Nissl substance (clumps of rough endoplasmic reticulum and free poly ribosomes) and DNA staining within the nucleus found in nerve cells. This method differentiate nerve cells from glia. With this methods the architectural structure of nerve cells can be well studied.
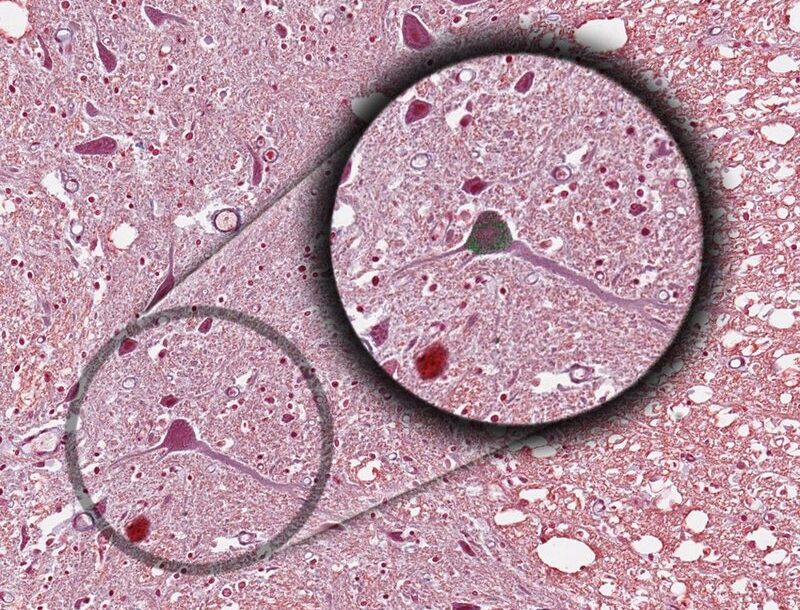
The Nissl stain is popular conventional light microscopic marker of neuronal cytoplasm. The merit of dye is it ability to selectively stain Nissl bodies of neurons. Consequently , the stain enables visualization of neurons against the pale neuropil or white matter backgrounds. Alteration in Nissl body staining is commonly interpreted in pathology as indication of neuronal injury.
Loss of Nissl can indicate the abnormalities such as cell damage or degeneration, which can lead to find disease.
In particular, the degree of maturation and functional state of neuronal cells are reflected by formational changes in the Nissl bodies (tigroid substance).
Nissl bodies are visible in the living neuron by phase contrast microscopy. Histochemical studies have shown that Nissl bodies are rich in ribonucleic acid, whilst E/M studies have shown that they consist of masses of rough-surfaced endoplasmic reticulum. highly organized in the form of flattened membranes enclosing cisternae. The membranes are fenestrated and intercommunicate. Their outer surfaces are studded with ribosomes; it is these which are responsible for the basiphilia noted with the optical microscope.
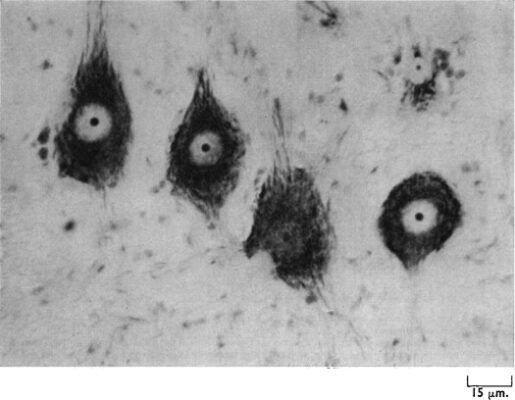
The most important defect of Nissl cresyl violet (Nissl stain) is that the exact morphology of the cells is not clearly visible with this method.
With this stain the nucleic acid looks blue-purple, while other parts with lower nucleic acid densities appear light bluish-gray.
The stain commonly used in this method is called cresyl echt violet acetate , which is mixed with distilled water in solution. It dyes Nissl dark blue or dark purple.
Procedure
- rehydrate the sample with distilled water.
- immerse in Cresyl Echt violet acetate for 2 minutes.
- Rinse the sample with distilled water.
- then dehydrate the sample with ethanol and clarify with xylene.
- Mount the section using a resinous medium.
Refrences
- https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/microscopy-and-microanalysis/article/nissl-staining-of-cat-spinal-cord-is-significantly-influenced-by-concentrations-of-glutaraldehyde-in-fixative/275170879372CCAC0C63FA16BDCB68BA
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/biochemistry-genetics-and-molecular-biology/nissl-body

 فارسی
فارسی