Education
Agitation with paraffin
Agitation with Paraffin (2 containers)
Agitation of tissue with paraffin is the fourth stage of tissue processing.
Agitation is a process in which the clarifying substance is replaced by paraffin or materials that completely fill the tissue cavities and make it thicker, making it easier to work with and sectioning the tissue.
This takes place using paraffin with 56-59 melting point and the volume of the paraffin used here should be 25-30 times the volume of tissue.
After the clarification stage, the tissues should be in Melted paraffin so that the paraffin penetrates deeply into the tissue and replaces the clarifying substance. Use two or three containers of molten paraffin and Slowly remove the tissue from the xylen and place it in each paraffin container for two hours.
The requirements of an ideal agitation environment are:
- Soluble in processing liquids
- Suitable for sectioning
- Ability to flatten after ribbon sectioning
- Melted at the temperature of 30-40 ° C.
- Transparent( colorless at melting point)
- Stable
- Uniform
- Non-Toxic
- Odorless
- Easy Usability
- Inexpensive
Paraffin
Wax paraffin is a polycrystalline mixture of solid hydrocarbons prepared by distilling coal and mineral oils. The melting point for this colorless ,white, clear & odorless paraffin is in wide range of (65-55)◦c. Tissue-wax adhesion Depends on the morphology of the agitation solution.
Crystals with same and small size provide better physical support to the specimens through latching The crystalline morphology of paraffin wax can be changed through additives.The resulting paraffin is less brittle ,It will be very uniform and with good sectioning properties, which will result in less deformation in thin sections. The wax paraffin commonly used as agitation medium is: cheap, safe, water-immiscible, high quality sections and usable in various aspects. Wax paraffin as a matrix leads to hardness and tissue support which prevents distortion and damage to the tissue samples and facilitates sectioning via microtome.
Tissue blocks can remain in tissue waxes for a long time without damage.
Disadvantage of wax paraffin is the long immersion time required for tissues such as bone, brain, eyes and …
Long immersion time Causes tissue shrinkage and hardening. All wax paraffin should be filtered regularly, If it Crystallize through the water content, water can be removed by heating and stirring.
Note:
Paraffin waxes with a low melting point are soft and suitable for tissues such as the fetus and areola. While paraffin waxes with high melting point, are hard, and suitable for tissues such as hard fibrosis.
Suitable Paraffin for histology:
.The properties of wax paraffin can be improved by histological purpose and by adding substances to it
- Improving the quality of sectioning Using heat-treated paraffin wax at high temperatures or use Microcrystalline paraffin wax.
- Increasing hardness: Adding stearic acid
- Reducing melting point: Adding Spermaceti or Phenanthrene
- Improving adhesion between sample and wax paraffin: by changing the morphology of crystalline by adding 5.0% Cersin, 0.1-0.5% Beeswax, rubber or Phenanthrene
Note:
Addition of stearic or palmic acid reduces the melting point of paraffin while maintaining hardness
Examples of modified paraffin waxes:
Paraplast: A mixture of very pure paraffin with thermoplastic polymers that has a high degree of elasticity and lead to High quality section results.
Paraplast plus: Also includes DMSO, which results in rapid penetration and uniform matrix, and Reduces immersion time and thus reduces tissue preparation time.
Ester waxes: have a low melting point (64 ° C), hard at room temperature, good adhesion properties, thin sections, No crushing during sectioning hard tissues.
Polyester wax: low melting point (83 ° C), reduced heat induction, suitable for HEAT-LABILE samples
In order to minimize heat hardening and an ideal environment for combining optical and electron microscopes.
Water-soluble waxes or PEGs: To study Temperature unstable lipids and proteins and solvents to overcome shrinkage Tissue, tissue damage and distortion in paraffin wax technique, a good technique for enzyme histochemistry.
Attention:
Polyethylene glycols are different lengths polymers at room temperature, liquid PEG600, soft PEG1000, hard PEG1500 and PEG4000 is hard and brittle. They are generally harder and denser than paraffin wax.
Attention:
The use of vacuum has no effect on sample dehydration and clarification, but greatly facilitates the paraffin phase. In devices that use vacuum in the last step, they prepare better fatty tissues like the brain.
Attention:
To reduce the time of Tissue Processing stir or heat the solution.
Tissue processors are stirring the tissue containers constantly in the solution, which causes better mixing so the time of dehydration, clarification and paraffinization of tissues reduces.
Heating facilitates the penetration of solutions into tissues by increasing kinetic energy, but changes the stainbility .but because the liquids used in the passage are all flammable The maximum recommended temperature is 45 degrees Celsius Use heating only when it is needed highly.
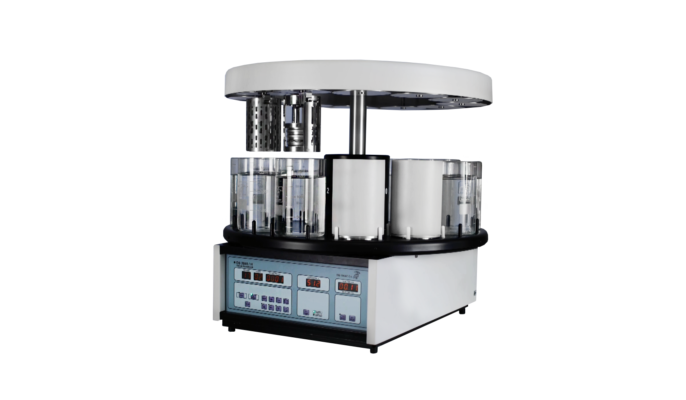
Did Sabz Tissue Processor for processing tissues

 فارسی
فارسی